Geometry package¶
In MCEq, geometry is everything related to the medium in which the particle
cascade develops. The very basic geometrical functions for the polar coordinate
system of the Earth - no it’s not flat, but just azimuth symmetric - are located
in MCEq.geometry.geometry. The density parameterizations and interfaces
are in MCEq.geometry.density_profiles
MCEq.geometry.density_profiles¶
This module includes classes and functions modeling the Earth’s atmosphere. Currently, two different types models are supported:
- Linsley-type/CORSIKA-style parameterization
- Numerical atmosphere via external routine (NRLMSISE-00)
Both implementations have to inherit from the abstract class
EarthsAtmosphere, which provides the functions for other parts of
the program. In particular the function EarthsAtmosphere.get_density()
Typical interaction:
$ atm_object = CorsikaAtmosphere("BK_USStd")
$ atm_object.set_theta(90)
$ print 'density at X=100', atm_object.X2rho(100.)
- The class
MCEqRunwill only the following routines:: EarthsAtmosphere.set_theta(),EarthsAtmosphere.r_X2rho().
If you are extending this module make sure to provide these functions without breaking compatibility.
- Example:
An example can be run by executing the module:
$ python MCEq/atmospheres.py
-
class
MCEq.geometry.density_profiles.AIRSAtmosphere(location, season, extrapolate=True, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Interpolation class for tabulated atmospheres.
This class is intended to read preprocessed AIRS Satellite data.
Parameters: - location (str) – see
init_parameters() - season (str,optional) – see
init_parameters()
-
get_density(h_cm)[source]¶ Returns the density of air in g/cm**3.
Interpolates table at requested value for previously set year and day of year (doy).
Parameters: h_cm (float) – height in cm Returns: density 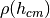 in g/cm**3
in g/cm**3Return type: float
- location (str) – see
-
class
MCEq.geometry.density_profiles.CorsikaAtmosphere(location, season=None)[source]¶ Class, holding the parameters of a Linsley type parameterization similar to the Air-Shower Monte Carlo CORSIKA.
The parameters pre-defined parameters are taken from the CORSIKA manual. If new sets of parameters are added to
init_parameters(), the array _thickl can be calculated usingcalc_thickl().-
_atm_param¶ (5x5) Stores 5 atmospheric parameters _aatm, _batm, _catm, _thickl, _hlay for each of the 5 layers
Type: numpy.array
Parameters: - location (str) – see
init_parameters() - season (str,optional) – see
init_parameters()
-
calc_thickl()[source]¶ Calculates thickness layers for
depth2height()The analytical inversion of the CORSIKA parameterization relies on the knowledge about the depth
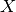 , where
trasitions between layers/exponentials occur.
, where
trasitions between layers/exponentials occur.Example
Create a new set of parameters in
init_parameters()inserting arbitrary values in the _thikl array:$ cor_atm = CorsikaAtmosphere(new_location, new_season) $ cor_atm.calc_thickl()
Replace _thickl values with printout.
-
depth2height(x_v)[source]¶ Converts column/vertical depth to height.
Parameters: x_v (float) – column depth 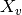 in g/cm**2
in g/cm**2Returns: height in cm Return type: float
-
get_density(h_cm)[source]¶ Returns the density of air in g/cm**3.
Uses the optimized module function
corsika_get_density_jit().Parameters: h_cm (float) – height in cm Returns: density 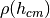 in g/cm**3
in g/cm**3Return type: float
-
get_mass_overburden(h_cm)[source]¶ Returns the mass overburden in atmosphere in g/cm**2.
Uses the optimized module function
corsika_get_m_overburden_jit()Parameters: h_cm (float) – height in cm Returns: column depth 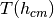 in g/cm**2
in g/cm**2Return type: float
-
init_parameters(location, season)[source]¶ Initializes
_atm_param. Parameters from ANTARES/KM3NET are based on the work of T. Heid (see this issue)location CORSIKA Table Description/season “USStd” 23 US Standard atmosphere “BK_USStd” 37 Bianca Keilhauer’s USStd “Karlsruhe” 24 AT115 / Karlsruhe “SouthPole” 26 and 28 MSIS-90-E for Dec and June “PL_SouthPole” 29 and 30 - Lipari’s Jan and Aug
“ANTARES/KM3NeT-ORCA” NA PhD T. Heid “KM3NeT-ARCA” NA PhD T. Heid Parameters: Raises: Exception– if parameter set not available
-
-
class
MCEq.geometry.density_profiles.EarthsAtmosphere(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Abstract class containing common methods on atmosphere. You have to inherit from this class and implement the virtual method
get_density().Note
Do not instantiate this class directly.
-
X2h(X)[source]¶ Returns the height above surface as a function of slant depth for currently selected zenith angle.
The spline s_lX2h is used, which was calculated or retrieved from cache during the
set_theta()call.Parameters: X (float) – slant depth in g/cm**2 Returns: height above surface in cm Return type: float h
-
X2rho(X)[source]¶ Returns the density
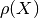 .
.The spline s_X2rho is used, which was calculated or retrieved from cache during the
set_theta()call.Parameters: X (float) – slant depth in g/cm**2 Returns: 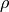 in cm**3/g
in cm**3/gReturn type: float
-
calculate_density_spline(n_steps=2000)[source]¶ Calculates and stores a spline of
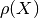 .
.Parameters: n_steps (int, optional) – number of 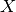 values
to use for interpolation
values
to use for interpolationRaises: Exception– ifset_theta()was not called before.
-
gamma_cherenkov_air(h_cm)[source]¶ Returns the Lorentz factor gamma of Cherenkov threshold in air (MeV).
-
get_density(h_cm)[source]¶ Abstract method which implementation should return the density in g/cm**3.
Parameters: h_cm (float) – height in cm Returns: density in g/cm**3 Return type: float Raises: NotImplementedError
-
h2X(h)[source]¶ Returns the depth along path as function of height above surface.
The spline s_X2rho is used, which was calculated or retrieved from cache during the
set_theta()call.Parameters: h (float) – vertical height above surface in cm Returns: X slant depth in g/cm**2 Return type: float
-
nref_rel_air(h_cm)[source]¶ Returns the refractive index - 1 in air (density parametrization as in CORSIKA).
-
r_X2rho(X)[source]¶ Returns the inverse density
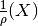 .
.The spline s_X2rho is used, which was calculated or retrieved from cache during the
set_theta()call.Parameters: X (float) – slant depth in g/cm**2 Returns: 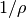 in cm**3/g
in cm**3/gReturn type: float
-
set_theta(theta_deg)[source]¶ Configures geometry and initiates spline calculation for
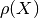 .
.If the option ‘use_atm_cache’ is enabled in the config, the function will check, if a corresponding spline is available in the cache and use it. Otherwise it will call
calculate_density_spline(), make the functionr_X2rho()available to the core code and store the spline in the cache.Parameters: theta_deg (float) – zenith angle 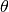 at detector
at detector
-
max_X Depth at altitude 0.
-
max_den¶ Density at altitude 0.
-
s_X2rho¶ Spline for conversion from depth to density.
-
s_h2X¶ Spline for conversion from altitude to depth.
-
s_lX2h¶ Spline for conversion from depth to altitude.
-
-
class
MCEq.geometry.density_profiles.GeneralizedTarget(len_target=100000.0, env_density=0.001225, env_name='air')[source]¶ This class provides a way to run MCEq on piece-wise constant one-dimenional density profiles.
The default values for the average density are taken from config file variables len_target, env_density and env_name. The density profile has to be built by calling subsequently
add_material(). The current composition of the target can be checked withdraw_materials()orprint_table().Note
If the target is not air or hydrogen, the result is approximate, since seconray particle yields are provided for nucleon-air or proton-proton collisions. Depending on this choice one has to adjust the nuclear mass in
mceq_config.Parameters: -
add_material(start_position_cm, density, name)[source]¶ Adds one additional material to a composite target.
Parameters: Raises: Exception– If requested start_position_cm is not properly defined.
-
draw_materials(axes=None, logx=False)[source]¶ Makes a plot of depth and density profile as a function of the target length. The list of materials is printed out, too.
Parameters: axes (plt.axes, optional) – handle for matplotlib axes
-
get_density(l_cm)[source]¶ Returns the density in g/cm**3 as a function of position l in cm.
Parameters: l (float) – position in target in cm Returns: density in g/cm**3 Return type: float Raises: Exception– If requested position exceeds target length.
-
get_density_X(X)[source]¶ Returns the density in g/cm**3 as a function of depth X.
Parameters: X (float) – depth in g/cm**2 Returns: density in g/cm**3 Return type: float Raises: Exception– If requested depth exceeds target.
-
r_X2rho(X)[source]¶ Returns the inverse density
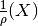 .
.Parameters: X (float) – slant depth in g/cm**2 Returns: 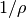 in cm**3/g
in cm**3/gReturn type: float
-
set_length(new_length_cm)[source]¶ Updates the total length of the target.
Usually the length is set
-
set_theta(*args)[source]¶ This method is not defined for the generalized target. The purpose is to catch usage errors.
Raises: NotImplementedError– always
-
max_X¶ Maximal depth of target.
-
s_X2h¶ Spline for depth at distance.
-
s_h2X¶ Spline for distance at depth.
-
-
class
MCEq.geometry.density_profiles.IsothermalAtmosphere(location, season, hiso_km=6.3, X0=1300.0)[source]¶ Isothermal model of the atmosphere.
This model is widely used in semi-analytical calculations. The isothermal approximation is valid in a certain range of altitudes and usually one adjust the parameters to match a more realistic density profile at altitudes between 10 - 30 km, where the high energy muon production rate peaks. Such parametrizations are given in the book “Cosmic Rays and Particle Physics”, Gaisser, Engel and Resconi (2016). The default values are from M. Thunman, G. Ingelman, and P. Gondolo, Astropart. Physics 5, 309 (1996).
Parameters:
-
class
MCEq.geometry.density_profiles.MSIS00Atmosphere(location, season=None, doy=None, use_loc_altitudes=False)[source]¶ Wrapper class for a python interface to the NRLMSISE-00 model.
NRLMSISE-00 is an empirical model of the Earth’s atmosphere. It is available as a FORTRAN 77 code or as a verson traslated into C by Dominik Borodowski. Here a PYTHON wrapper has been used.
-
_msis¶ NRLMSISE-00 python wrapper object handler
Parameters: - location (str) – see
init_parameters() - season (str,optional) – see
init_parameters()
-
get_density(h_cm)[source]¶ Returns the density of air in g/cm**3.
Wraps around ctypes calls to the NRLMSISE-00 C library.
Parameters: h_cm (float) – height in cm Returns: density 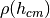 in g/cm**3
in g/cm**3Return type: float
-
get_temperature(h_cm)[source]¶ Returns the temperature of air in K.
Wraps around ctypes calls to the NRLMSISE-00 C library.
Parameters: h_cm (float) – height in cm Returns: density 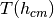 in K
in KReturn type: float
-
init_parameters(location, season, doy, use_loc_altitudes)[source]¶ Sets location and season in
NRLMSISE-00.Translates location and season into day of year and geo coordinates.
Parameters:
-
set_doy(day_of_year)[source]¶ Changes MSIS season by day of year.
Parameters: day_of_year (int) – - Jan.=0, 1.Feb=32
-
set_location(location)[source]¶ Changes MSIS location by strings defined in _msis_wrapper.
Parameters: location (str) – location as defined in NRLMSISE-00.
-
set_location_coord(longitude, latitude)[source]¶ Changes MSIS location by longitude, latitude in _msis_wrapper
Parameters:
-
-
class
MCEq.geometry.density_profiles.MSIS00IceCubeCentered(location, season)[source]¶ Extension of
MSIS00Atmospherewhich couples the latitude setting with the zenith angle of the detector.Parameters: -
latitude(det_zenith_deg)[source]¶ Returns the geographic latitude of the shower impact point.
Assumes a spherical earth. The detector is 1948m under the surface.
Credits: geometry fomulae by Jakob van Santen, DESY Zeuthen.
Parameters: det_zenith_deg (float) – zenith angle at detector in degrees Returns: latitude of the impact point in degrees Return type: float
-
set_theta(theta_deg)[source]¶ Configures geometry and initiates spline calculation for
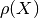 .
.If the option ‘use_atm_cache’ is enabled in the config, the function will check, if a corresponding spline is available in the cache and use it. Otherwise it will call
calculate_density_spline(), make the functionr_X2rho()available to the core code and store the spline in the cache.Parameters: theta_deg (float) – zenith angle 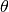 at detector
at detector
-
MCEq.geometry.geometry¶
The module contains the geometry for an azimuth symmetric Earth.
-
class
MCEq.geometry.geometry.EarthGeometry[source]¶ - A model of the Earth’s geometry, approximating it
- by a sphere. The figure below illustrates the meaning of the parameters.
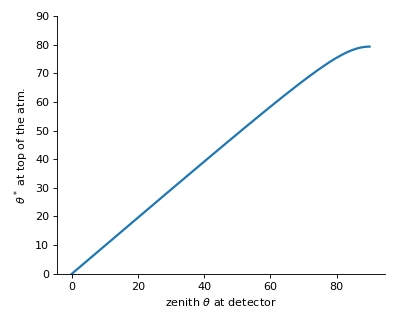
Example
The plots below will be produced by executing the module:
$ python geometry.py
-
cos_th_star(theta)[source]¶ Returns the zenith angle at atmospheric boarder
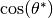 in [rad] as a function of zenith at detector.
in [rad] as a function of zenith at detector.
-
MCEq.geometry.geometry.chirkin_cos_theta_star(costheta)[source]¶ 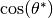 parameterization.
parameterization.This function returns the equivalent zenith angle for for very inclined showers. It is based on a CORSIKA study by D. Chirkin, hep-ph/0407078v1, 2004.
Parameters: costheta (float) – 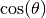 in [rad]
in [rad]Returns: 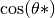 in [rad]
in [rad]Return type: float
MCEq.geometry.nrlmsise00¶
CTypes interface to the C-version of the NRLMSISE-00 code, originally developed by Picone et al.. The C-translation is by Dominik Brodowski <https://www.brodo.de/space/nrlmsise/index.html>_.
MCEq.geometry.corsikaatm¶
This set of functions are C implementations of the piecewise defined exponential profiles as used in CORSIKA. An efficient implementation is difficult in plain numpy.
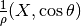 cm**3/g
cm**3/g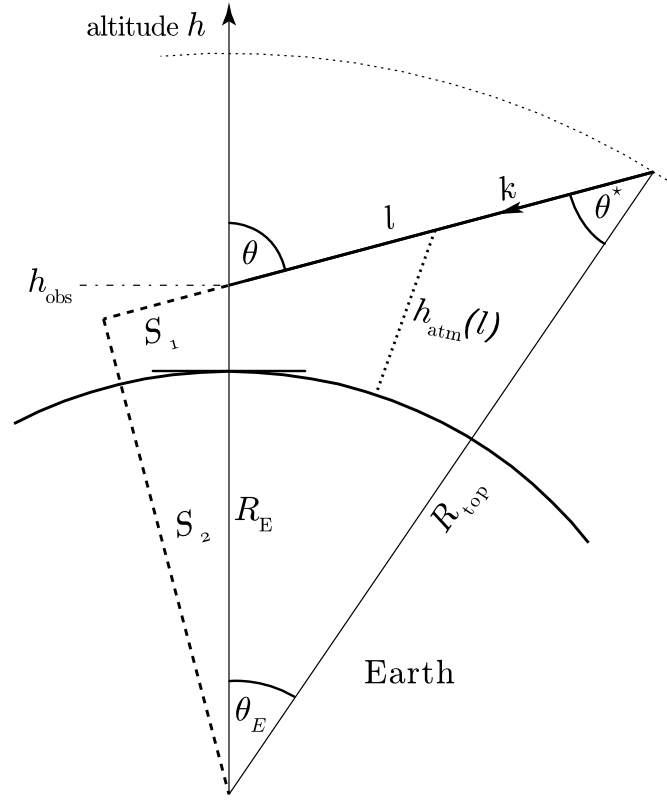
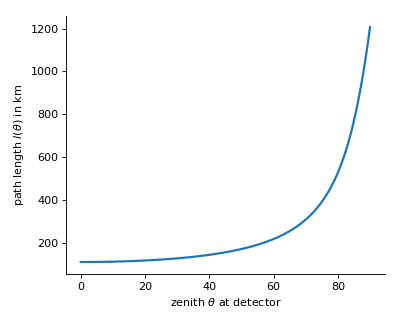
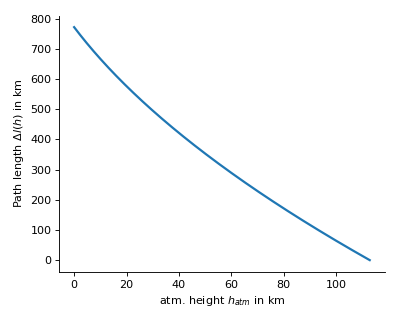
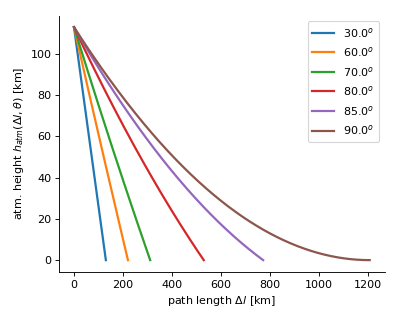
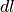 covered along path
covered along path 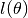 as a function of current height. Inverse to
as a function of current height. Inverse to